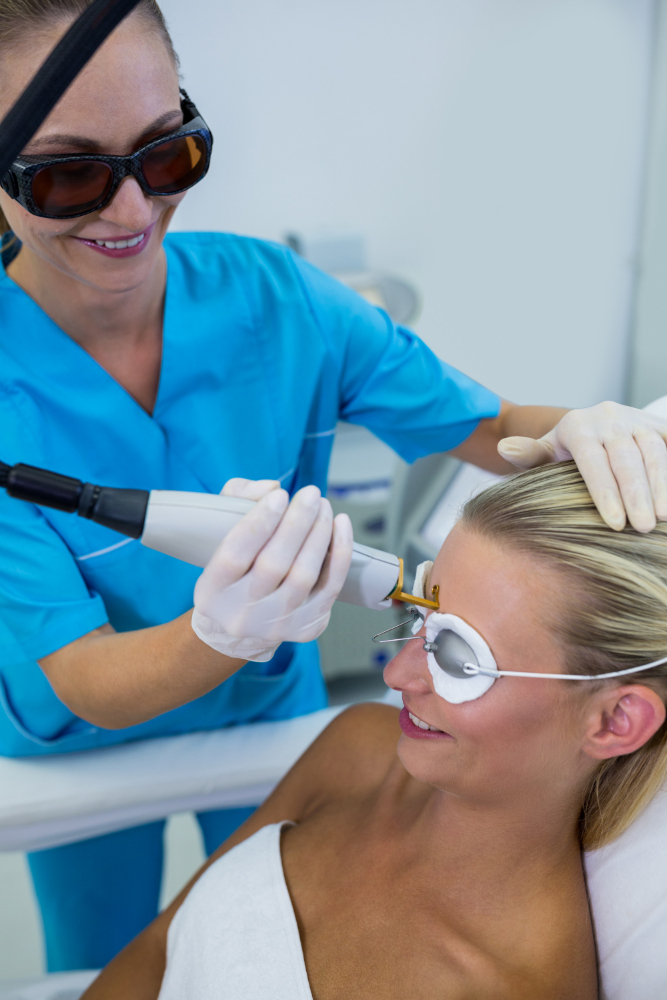
Laser resurfacing and skin rejuvenation treatments use laser technology to address various skin concerns and improve skin texture, tone, and overall appearance. These treatments work by stimulating collagen production, reducing wrinkles and fine lines, minimizing skin discoloration, and promoting skin renewal. Here are some common laser resurfacing and skin rejuvenation techniques:
1. Fractional Laser Resurfacing: Fractional laser resurfacing delivers tiny, focused beams of laser light to target small areas of the skin, leaving surrounding tissue intact. This approach stimulates collagen production and promotes the growth of new, healthy skin cells, resulting in smoother texture, reduced wrinkles, and improved skin tone. Fractional lasers are effective for treating fine lines, acne scars, sun damage, and uneven pigmentation.
2. CO2 Laser Resurfacing: CO2 laser resurfacing is a more aggressive form of laser treatment that removes layers of damaged skin to reveal smoother, rejuvenated skin underneath. This procedure is particularly effective for deeper wrinkles, pronounced facial lines, and moderate to severe sun damage. CO2 laser resurfacing can produce significant improvements in skin texture and tone but may require a more extended recovery period compared to fractional laser treatments.
3. Erbium Laser Resurfacing: Erbium laser resurfacing is a milder alternative to CO2 laser treatment, making it suitable for individuals with lighter skin tones and less severe skin concerns. Erbium lasers target the outermost layers of the skin, stimulating collagen production and promoting skin renewal. This approach results in smoother, firmer skin with reduced wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. Erbium laser resurfacing typically involves a shorter recovery time compared to CO2 laser treatment.
4. Non-Ablative Laser Therapy: Non-ablative laser therapy uses lower-energy laser beams to heat the deeper layers of the skin without damaging the surface. This stimulates collagen production and improves skin elasticity, firmness, and texture. Non-ablative lasers are less invasive than ablative treatments and are suitable for individuals with mild to moderate skin concerns. Multiple treatment sessions may be required to achieve optimal results.
5. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: IPL therapy, also known as photofacial or photorejuvenation, uses broad-spectrum light energy to target and correct various skin imperfections, including sun damage, age spots, redness, and uneven pigmentation. IPL treatments are non-invasive and can effectively improve overall skin tone and clarity with minimal downtime. They are often used to rejuvenate the face, neck, chest, and hands.
6. Fractional Radiofrequency (RF) Microneedling: Fractional RF microneedling combines radiofrequency energy with microneedling to deliver controlled thermal energy deep into the skin’s dermal layers. This stimulates collagen production and promotes skin tightening, smoothing, and rejuvenation. Fractional RF microneedling is effective for treating wrinkles, acne scars, enlarged pores, and overall skin laxity.
7. Laser Skin Tightening: Laser skin tightening treatments use infrared laser energy to heat the skin’s deeper layers, stimulating collagen remodeling and tissue contraction. This leads to firmer, more toned skin and a reduction in wrinkles and sagging. Laser skin tightening is commonly performed on the face, neck, and body and is suitable for individuals seeking non-surgical skin rejuvenation with minimal downtime.
Before undergoing laser resurfacing or skin rejuvenation treatment, it’s essential to consult with a qualified dermatologist or skincare specialist to assess your skin condition, discuss treatment options, and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs and goals. They can help determine the most suitable laser technology and treatment approach based on your skin type, concerns, and desired outcomes. Additionally, following pre-treatment and post-treatment care instructions is crucial to ensure optimal results and minimize the risk of complications.

