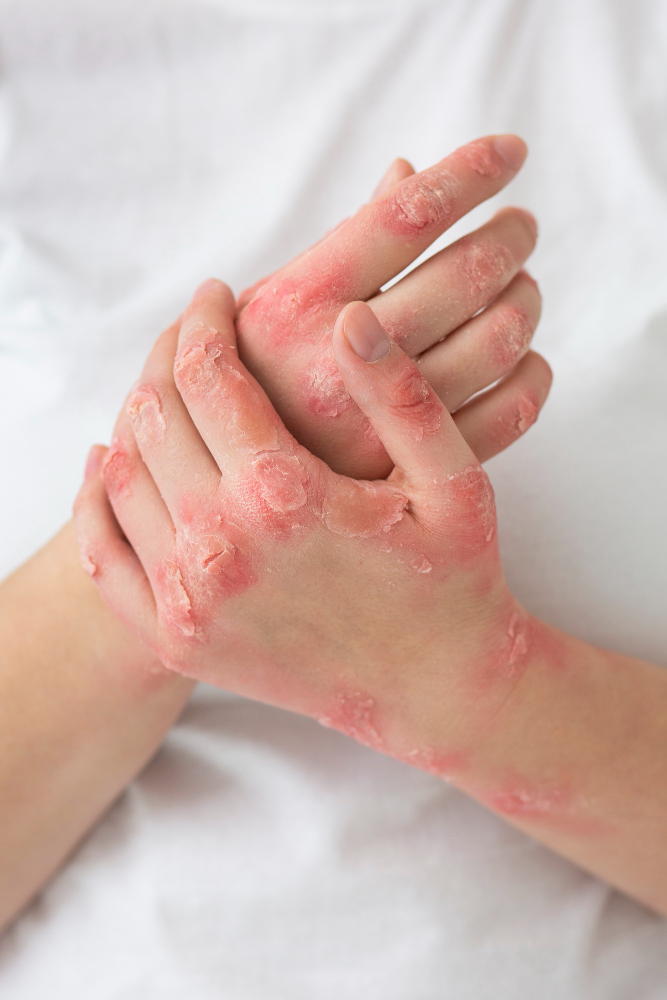
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing it to develop red, scaly patches. Here’s an overview of psoriasis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options:
1. Causes: Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid turnover of skin cells. The exact cause of this immune system malfunction is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
2. Symptoms: The most common symptom of psoriasis is the development of raised, red patches of skin covered with silvery scales. These patches, known as plaques, can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Other symptoms may include itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas.
3. Types: There are several types of psoriasis, including:
– Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red plaques covered with silver scales.
– Guttate Psoriasis: Small, red spots that often appear after a bacterial or viral infection.
– Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, red patches that develop in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, or under the breasts.
– Pustular Psoriasi White, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin.
– Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare and severe form that causes widespread redness and scaling of the skin.
4. Triggers: Psoriasis symptoms may worsen or flare up in response to certain triggers, including stress, infections, injuries to the skin, cold weather, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, certain medications (such as lithium or beta-blockers), and hormonal changes.
5. Treatment: While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment may include:
– Topical Treatments: Creams, ointments, or shampoos containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, or coal tar.
– Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision, either with natural sunlight or artificial light sources.
– Systemic Medications: Oral or injectable medications that work throughout the body to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics.
– Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
6. Complications: Psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of developing other health conditions, including psoriatic arthritis (a type of inflammatory arthritis affecting the joints), cardiovascular disease, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and depression.
7. Management: Psoriasis is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and regular follow-up with a healthcare provider. With proper treatment and self-care measures, many people with psoriasis can effectively control their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.

